In some cases, people may experience an infection after a tooth extraction, even if they weren't infected before. This is due to the presence of bacteria in the mouth, which can become more active after a tooth is removed. To treat an infection that occurs after a tooth extraction, it is important to consult a dentist who can prescribe antibiotics. The dentist will first need to perform an examination to understand what is happening in the patient's mouth.
Then, they will decide which antibiotic best suits their needs. Fortunately, the chances of infection are low, but it is important to be aware of any symptoms that may arise. In some cases, complications can arise after a tooth extraction, such as getting a bone infection (which is unlikely). A dentist may recommend tooth extraction for various reasons and it can be performed on any tooth inside the mouth.
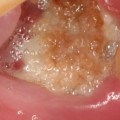
When a tooth is extracted, it leaves a hole in the upper or lower jaw which needs to coagulate to prevent infection. Extracting a tooth itself involves a minimally invasive procedure that is quickly performed in the dental chair. If any symptoms occur after the extraction, it is important to tell your dentist right away. Maintaining natural teeth is always the top priority, but there are times when a tooth extraction is necessary and it will be the best option.
It is important to consider any potential complications that may arise after a tooth extraction. By consulting with your dentist and following their instructions, you can reduce your risk of infection and other complications.